- Antenna for FZ-M1 4G GPS
- Configuring the FZ-M1 for GPS
- Configure EM7355 GPS
- Output GPS Strings to gpsd
In this part, now that ModemManager isn’t interfering, verify the onboard GPS and the qmi-to-gps link is enabled. We do this with AT (attention) commands. One of the oldest (maybe THE oldest?) method of sending instruction to a modem.
AT terminals are accessed across whatever /dev/tty device they are assigned using the socat command. Refer back to the ports: output of the mmcli -m command from the last post. My AT is running on /dev/ttyUSB2.
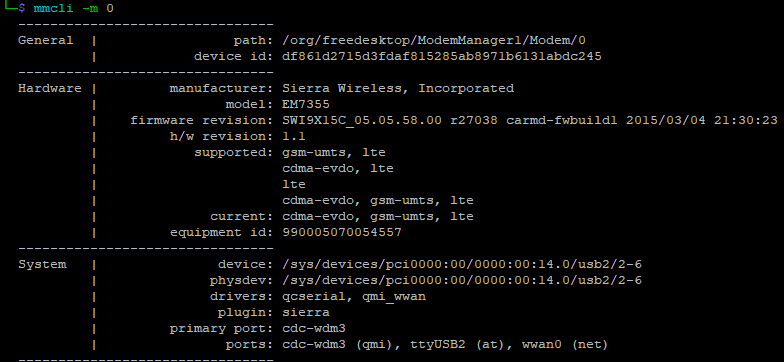
So to access it I run:

That blank line is the only feedback received. To verify you are actually talking to the modem start with just sending AT. You should get an OK response:
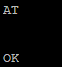
If you get a bunch of repeating output, then something called command echo is activated. You can turn off the command echo with ATE0. You’ll get a repeat the when you run it but that will be the end of it.

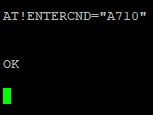
Some commands require a password to run. Quick google search reveals default passcode is A710. Bear in mind this could have been changed at some point (however unlikely). Sending the passcode unlocks all the protected commands for the duration of the session. So you only need to run it once each time you connect with socat.
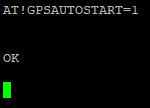
Make sure the device is set to start its GPS module on boot:
Then tell it to allow QMI interface to send/receive commands for GPS:
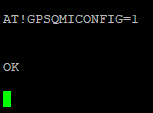
Reboot the modem so the changes take effect:
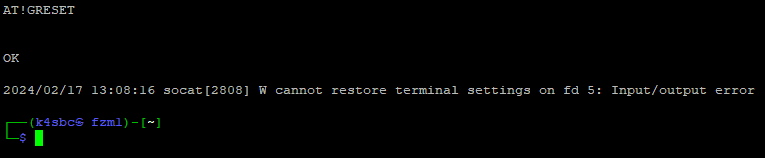
The reboot kicks you back to the terminal window. It usually takes a couple minutes for the modem to cycle so grab a drink before the next step.